How to Diagnose Tuberculosis in Infants

Tuberculosis (TB) is a bacterial infection that can affect any part of the body, but most commonly affects the lungs. TB is spread through the air when someone with active TB coughs, sneezes, or talks. Infants are particularly vulnerable to TB because their immune systems are not fully developed.
The symptoms of TB in infants can be nonspecific, making it difficult to diagnose. However, there are a few key symptoms that may suggest TB in an infant:
Fever
Cough
Weight loss
Poor feeding
Irritability
Lethargy
If you are concerned that your infant may have TB, it is important to see a doctor right away. The doctor will perform a physical examination and ask about your infant's symptoms. The doctor may also order one or more of the following tests to confirm a diagnosis of TB:
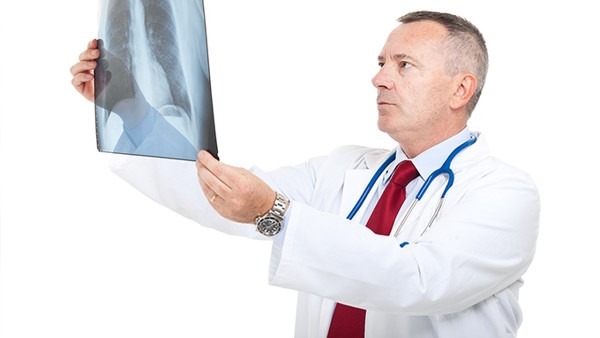
Chest X-ray: A chest X-ray can show if there are any abnormalities in the lungs that may be consistent with TB.
Sputum culture: A sputum culture is a test that checks for the presence of TB bacteria in the sputum.
Blood test: A blood test can check for antibodies to TB bacteria.
Tuberculin skin test: A tuberculin skin test is a test that checks for the presence of TB bacteria in the body.
If your infant is diagnosed with TB, the doctor will start treatment right away. Treatment for TB typically involves taking antibiotics for several months. It is important to complete the full course of treatment to prevent the TB from becoming resistant to antibiotics.
Preventing TB in Infants
The best way to prevent TB in infants is to make sure that they are vaccinated against TB. The TB vaccine is a safe and effective way to protect infants from TB. The vaccine is typically given at birth or shortly thereafter.
In addition to vaccination, there are other things you can do to help prevent TB in your infant:
Avoid contact with people who have active TB.
If you are exposed to someone with active TB, tell your doctor right away.
Keep your infant's environment clean and free of dust and other allergens.
Make sure your infant gets plenty of rest and nutrition.
If you have any questions about TB in infants, please talk to your doctor.
What is TB?
TB is a bacterial infection that can affect any part of the body, but most commonly affects the lungs. TB is spread through the air when someone with active TB coughs, sneezes, or talks.
What are the symptoms of TB in infants?
The symptoms of TB in infants can be nonspecific, making it difficult to diagnose. However, there are a few key symptoms that may suggest TB in an infant:
Fever
Cough
Weight loss
Poor feeding
Irritability
Lethargy
How is TB diagnosed in infants?
The doctor will perform a physical examination and ask about your infant's symptoms. The doctor may also order one or more of the following tests to confirm a diagnosis of TB:
Chest X-ray
Sputum culture
Blood test
Tuberculin skin test
How is TB treated in infants?
Treatment for TB typically involves taking antibiotics for several months. It is important to complete the full course of treatment to prevent the TB from becoming resistant to antibiotics.
How can I prevent TB in my infant?
The best way to prevent TB in infants is to make sure that they are vaccinated against TB. The TB vaccine is a safe and effective way to protect infants from TB. The vaccine is typically given at birth or shortly thereafter.
In addition to vaccination, there are other things you can do to help prevent TB in your infant:
Avoid contact with people who have active TB.
If you are exposed to someone with active TB, tell your doctor right away.
Keep your infant's environment clean and free of dust and other allergens.
Make sure your infant gets plenty of rest and nutrition.
The above is all the content that the editor wants to share with you. I sincerely hope that these contents can bring some help to your life and health, and I also wish that your life will be happier and happier.
Topic: #diagnose #to #how